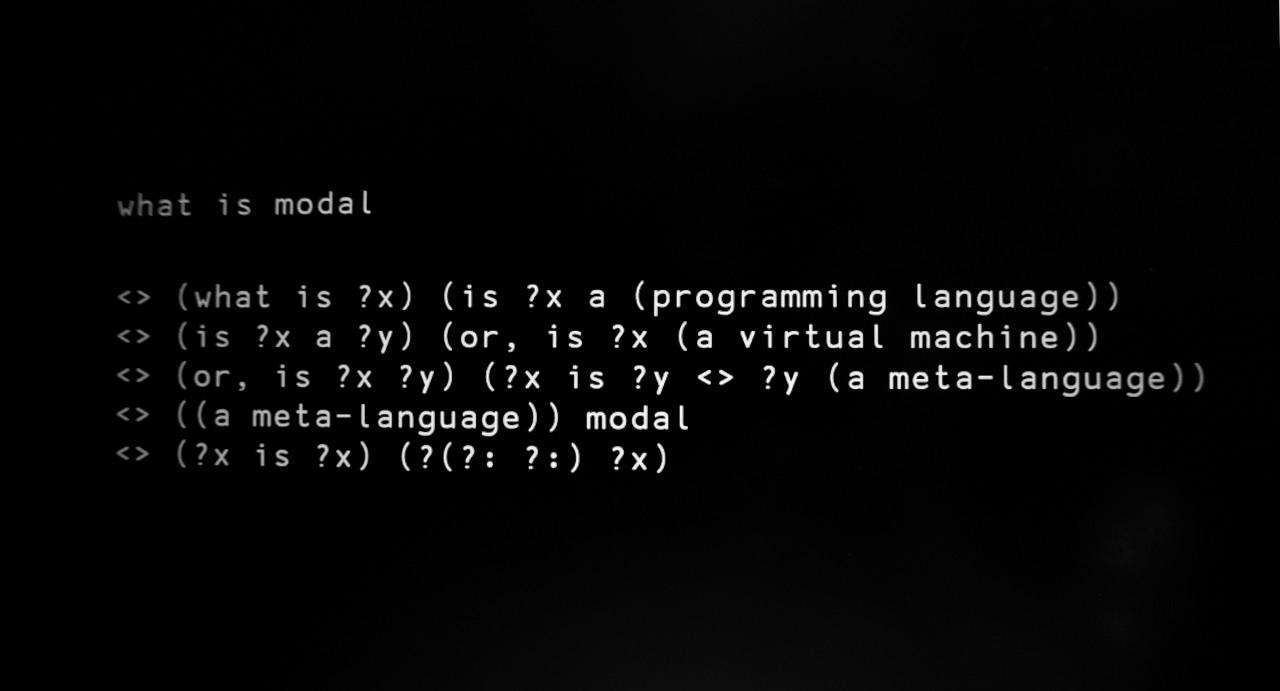
Modal is a tree rewriting system.

Modal programs are represented as a series of substitution rules, applied to a given tree which gets continually modified until no rules match any given part of the tree. The two principal elements of Modal are:
The documentation below displays the examples as a series of rules, followed by the rewriting steps in the following format:
<> (Let's learn Modal!) This is a comment <> (hello) (good bye) This is a rule
(hello) world This is the input (good bye) world This is the result
Playground
Evaluation is done by scanning from left-to-right across a string that represents a serialized tree. Rules are tested against each node, when a match occurs, the left-hand side of the matching pattern is erased from the tree, the right-hand side of the rule is written in its stead, and scanning starts over at the start of the tree. The evaluation ends when no rule match.
Rules
To define a new rule, start with <>, followed by a left and a right statement, which is either a word, or a tree. The program evaluation starts at the first character of the string and walks through to the end trying to match a transformation rule from that location:
<> (a bat) (a black cat) <> (a person) (a bat)
(I am (a person)) (I am (a bat)) (I am (a black cat))
Modal is homoiconic, meaning that any string is a potential program and new rules can be composed directly during the evaluation.
Registers
Registers are ? prefixed identifiers bound to an address in a pattern used in rewriting. When a register is used in a pattern, and when we try to match a given tree with a pattern, each register is bound to a corresponding address to the left-side of the rule, and referenced to the right-side of the rule:
<> (copy ?a) (?a ?a) <> (swap ?x ?y) (?y ?x)
(copy cat) (swap bat rat) (cat cat) (swap bat rat) (cat cat) (rat bat)
When a register appears more than once in a rule, each instance is bound to the first address, but differently named registers can still match on the same pattern:
<> (compare ?x ?x) (same) <> (compare ?x ?y) (different)
(compare cat bat) (compare rat rat) (different) (compare rat rat) (different) (same)
Logic
Equality in logic can be implemented by defining the truth table the comparison as shown above, for binary logic we can expand on the idea:
<> (and #t #t) #t <> (or #t #t) #t <> (and #t #f) #f <> (or #t #f) #t <> (and #f #t) #f <> (or #f #t) #t <> (and #f #f) #f <> (or #f #f) #f <> (not #t) #f <> (not #f) #t
(not (and #t #f)) (not #f) #t
Building on the comparison rule above, we can write conditionals with a ternary statement:
<> (ife #t ?t ?f) ?t <> (ife #f ?t ?f) ?f <> (print ?:) ()
(ife #t (print True) (print False)) (print True)
True?:
Events are handled by special registers with IO capabilities, for example, the ?: emits a symbol to the console. Here is a little program that prints letters in a list.
<> (putrec (?: ?x)) (putrec ?x) <> (putrec (?:)) (done.)
(putrec (a (b (c (d (e)))))) (putrec (b (c (d (e))))) (putrec (c (d (e)))) (putrec (d (e))) (putrec (e)) (done.)
abcde?:
When giving a quoted symbol, like (0), to the ?: register, the value printed will be the depth of nesting.
<> (Get the result of: 3 + 2) <> ((?a) + ?b) (?a + (?b)) <> (0 + ?b) (sum ?b) <> (print (sum ?:)) ()
(print (add (((0))) ((0))))
5?:
Numbers
0, for 0(0), for 1((0)), for 2(((0))), for 3((((0))), for 4
Internally, Modal has no built-in arithmetic and represents numbers as the symbol 0 wrapped in a number of parentheses equal to its value. Luckily arithmetic operations can be re-created with rewrite rules, for example, here's a little program that calculates the difference of two numbers, by gradually removing the wrapping parentheses on both operands:
<> (Get the result of: 5 - 2) <> ((?a) - (?b)) (?a - ?b) <> (?a - 0) (difference ?a) <> (print (difference ?:)) (done.)
(print (5 - 2)) (print (((((0)))) - (0))) (print ((((0))) - 0)) (print (difference (((0))))) (done.)
3?:
Notice how Modal has neither a prefix, infix or postfix notation, it is merely defined within the rules. The Modal number encoding allows to do comparison between numbers and with it we can implement FizzBuzz:
<> ((print-word ?:) ?i ?f ?b) ((print-line \n) ?i ?f ?b) <> ((print-line ?:) ?i ?f ?b) ((?i) (?f) (?b)) <> (100 ?f ?b) (done.) <> (?i 3 5) ((print-word FizzBuzz) ?i 0 0) <> (?i 3 ?b) ((print-word Fizz) ?i 0 ?b) <> (?i ?f 5) ((print-word Buzz) ?i ?f 0) <> (?i ?f ?b) ((print-word ?i) ?i ?f ?b)
(0 0 0)
0
1
2
Fizz
4
Buzz
Fizz
7
8
Fizz
Buzz
11
Fizz
13
14
FizzBuzz..?:
Loops
In the absence of familiar programming prefabs like for() and
while(), it's normal to wonder how to replicate behaviors from
other programming languages. By defining the end case as a rule above the
incrementing rule, the program will effectively loop until the end case is
met:
<> (spring 3) (Three years later.) <> (spring ?year) (summer ?year) <> (summer ?year) (autumn ?year) <> (autumn ?year) (winter ?year) <> (winter ?year) (spring (?year))
(spring 0) (summer 0) (autumn 0) (winter 0) (spring (0)) (summer (0)) (autumn (0)) (winter (0)) (spring ((0))) (summer ((0))) (autumn ((0))) (winter ((0))) (spring (((0)))) (Three years later.)
Types
Understanding how to use type guards, which are just symbols like any other, to orchestrate a specific evaluation order is important to become proficient with Modal. Creating a type system is merely a matter of using stricter rules expecting a specific symbol. Notice in the example below, how the print rule expects a specific type of data before firing despite being declared first:
<> (print (Name ?:)) (done.) <> (get-name) (Name Eva)
(print (get-name)) (print (Name Eva)) (done.)
Eva?:
Lists
Lastly, the ideal data structure in Modal is a list, like (foo(bar (baz
()))), this gives more flexibility so that rewrite rules can be applied
to on items of an unknown length, in comparison with a tuple, like (foo bar baz), in which
the exact number of items must be known beforehand.
<> (reverse List (?x ?y) ?z) (reverse List ?y (?x ?z)) <> (reverse List ?empty ?list) (print List ?list) <> (print List (?: ?x)) (print List ?x) <> (print List ()) (done.)
(reverse List (m (o (d (a (l ()))))) ()) (reverse List (o (d (a (l ())))) (m ())) (reverse List (d (a (l ()))) (o (m ()))) (reverse List (a (l ())) (d (o (m ())))) (reverse List (l ()) (a (d (o (m ()))))) (reverse List () (l (a (d (o (m ())))))) (print List (l (a (d (o (m ())))))) (print List (a (d (o (m ()))))) (print List (d (o (m ())))) (print List (o (m ()))) (print List (m ())) (print List ()) (done.)
ladom?:
Here's something a bit more interesting, to find an item in a list, we move a cursor in and out of it. The program trace shows that the rule matches a symbol that goes deeper into the list, modifies itself and returns with the result symbol. This sort of mechanical transformation of programs is typical in Modal.
<> ((find ?target) ?target (?next ?tail)) ((found ?target) ?next ?tail) <> ((find ?target) ?head (?next ?tail)) (?head ((find ?target) ?next ?tail)) <> ((find ?target) ?head ()) ((unfound ?target) ?head ()) <> (?head ((found ?target) ?next ?tail)) ((found ?target) ?head (?next ?tail)) <> (?head ((unfound ?target) ?next ?tail)) ((unfound ?target) ?head (?next ?tail))
((find e) a (b (c (d (e (f (g (h ())))))))) (a ((find e) b (c (d (e (f (g (h ())))))))) (a (b ((find e) c (d (e (f (g (h ())))))))) (a (b (c ((find e) d (e (f (g (h ())))))))) (a (b (c (d ((find e) e (f (g (h ())))))))) (a (b (c (d ((found e) f (g (h ()))))))) (a (b (c ((found e) d (f (g (h ()))))))) (a (b ((found e) c (d (f (g (h ()))))))) (a ((found e) b (c (d (f (g (h ()))))))) ((found e) a (b (c (d (f (g (h ())))))))
That's it! I hope you enjoy exploring this strange programming language.

modal(adj.): of, or relating to structure as opposed to substance.
- View Sources, Uxntal.
- Discord channel
- Levels of Dynamic behavior in Modal
- This language is an original creation of wryl from 2018, who has courteously spent countless hours to help me progress with the language, much of the code above is derived from their research and merely made available here as to give this fantastic system a home on the internet.
incoming: rewriting fractran vera thuesday 2025 2024 malleable computing